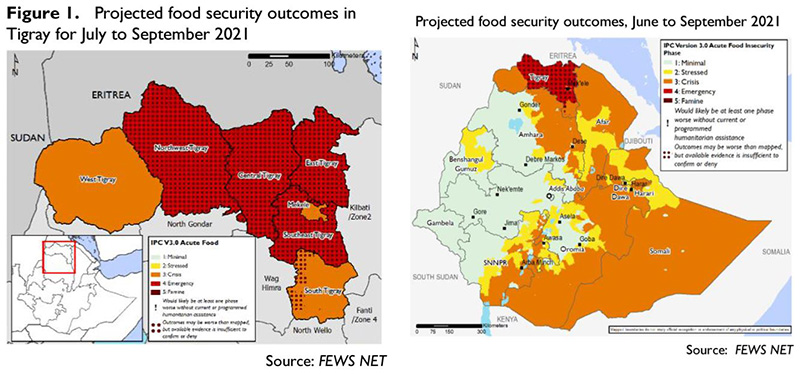
The cost of war for Ethiopians is not just felt on the battlefront or even the millions now displaced but in the ransacking of the future of young Ethiopians who once believed in future prosperity. The dream of Ethiopia to escape poverty is rapidly fading. While Ethiopian diaspora who are rarely Tigray and Oromo tout Abiy Ahmed as a prophetic bringer of fortune and power the opposite is becoming clear. The economy of Ethiopia is diving into a bottomless abyss beginning when Abiy Ahmed took power in 2018 with an increasingly accelerating progression downward.
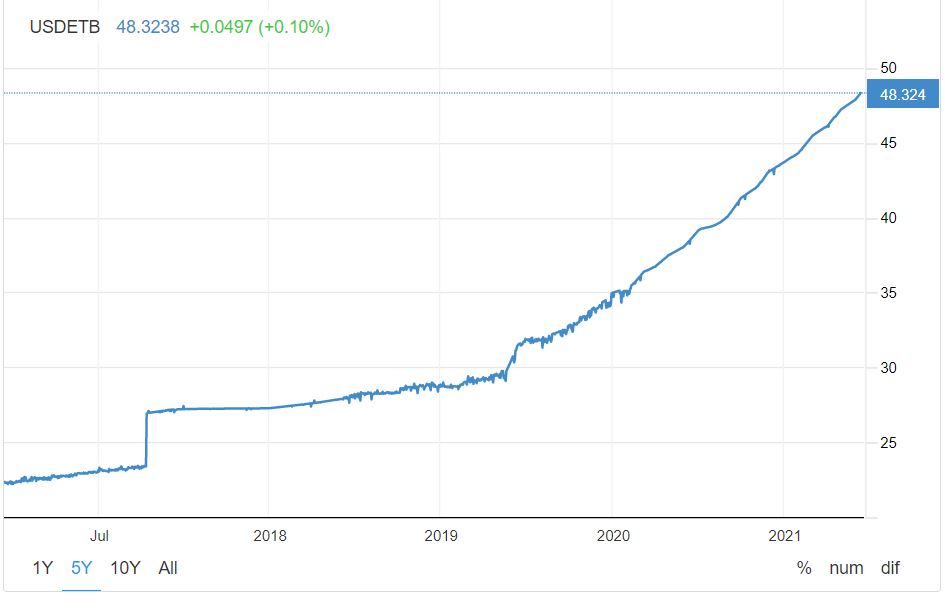
The Ethiopian birr has fallen in value by almost 50% since 2018. Noted Johns Hopkins economist Steven Hanke as well as others note that the current inflation rate of 31% which predicts will lead to an unbearable circumstance for the average Ethiopian.
Total Ethiopian gold reserves were at over $ 400 million when Abiy Ahmed took power in 2018 but now are likely below $100 million after payments to Eritrea, United Arab Emirates, Iran and others for weapons.
The Biden administration has clearly stated that it no longer considers the government under Abiy Ahmed a democracy. The free trade agreement, African Growth and Opportunity Act, with Ethiopia was dependent upon Ethiopia following democratic principals mutually agreed upon which were violated. Similarly many Western democracies are taking a similar view.
Although the Ethiopian government falsely claimed economic growth rates of 6% the real number is more like -2% and dropping. The human rights violations and the instability of the Ethiopian state by an ongoing war with no end coming on the horizon severely inhibits foreign investors from participating in the Ethiopian economy which at this point has no future.